MTH1005 Probability and Statistics (Cheat Sheet)
MTH1005 Probability and Statistics Cheat Sheet by William Fayers :)
Basic Probability Concepts
- Multiplicative Rule of Probability:
- Independent Events: .
- Dependent Events: .
- Conditional Probability: .
- Total Probability Law: .
- Bayes’ Formula: .
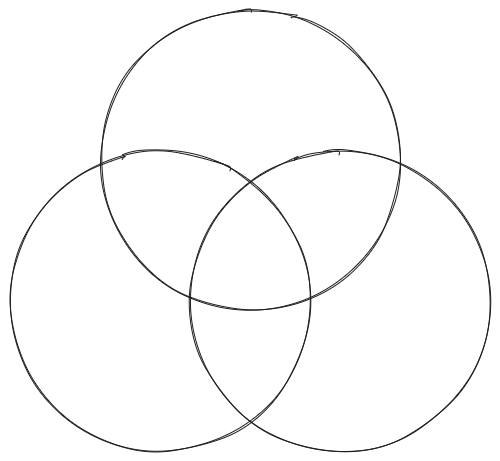
Useful empty Venn diagram for probability visualisation (to understand questions & their solutions):
Random Variables
- Discrete Random Variables: Ensure probabilities of all outcomes sum to 1.
- Probability Mass Functions (PMF): .
- Cumulative Distribution Functions (CDF): .
- Continuous Random Variables: Probabilities over intervals, not points.
- Probability Density Functions (PDF): .
- CDF for Continuous Variables: .
Statistical Measures
- Expectation and Variance:
- Expectation Value: or .
- Variance: or .
- Mappings: , .
- Joint Random Variables:
- Joint PMF: .
- Joint PDF: .
- Marginal Distributions: Derived from joint distribution by integrating out other variables.
- Covariance and Correlations:
- Covariance: .
- Correlation: .
Data Analysis
- Median and Quantiles:
- Median: Middle value of sorted data.
- Quantiles (Quartiles and Percentiles): Divide data into intervals with equal probabilities.
- Interquartile Distance (IQR): .
- Inequalities:
- Markov’s and Chebyshev’s Inequalities:
- Markov: .
- Chebyshev: .
- Markov’s and Chebyshev’s Inequalities:
Common Distributions
1. Uniform Distribution
- Expectation (Mean):
- Variance:
- Probability Mass Function (PMF): Every outcome within the range from to is equally likely.
2. Geometric Distribution
- Expectation (Mean):
- Variance:
- Probability Mass Function (PMF): Represents the probability of getting the first success on the -th trial.
3. Exponential Distribution
- Expectation (Mean):
- Variance:
- Probability Density Function (PDF): Describes the time between events in a Poisson point process.
4. Normal Distribution
- Expectation (Mean):
- Variance:
- Probability Density Function (PDF): Common for continuous data clustering around a mean.
5. Poisson Distribution
- Expectation (Mean):
- Variance:
- Probability Mass Function (PMF): Suitable for modelling the frequency of events within a fixed interval.
6. Binomial Distribution
- Expectation (Mean):
- Variance:
- Probability Mass Function (PMF): Describes the number of successes in a series of independent Bernoulli trials.
Decision Guide for Distributions
- Outcomes type:
- Discrete: Focuses on distinct, separate outcomes. Go to Step 2.
- Continuous: Concerns measurable quantities that can vary. Go to Step 4.
- Trial Independence:
- Independent with two outcomes: Each outcome doesn’t affect the others, with success/failure options. Go to Step 3.
- Not independent or different outcomes: Outcomes affect each other or there are multiple types of outcomes. Go to Step 5.
- Number of trials and interest in successes:
- Known trials and interest in successes: Binomial Distribution, used when the number of trials and the desire to determine the number of specific outcomes (like successes) is known.
- Interest in number of trials for first success: Geometric Distribution, applies when focusing on the count of trials needed to achieve a first success.
- Time or space between events:
- Events over time/space: Exponential Distribution, ideal for modelling time between continuous, independent events.
- Data clustering around mean: Normal Distribution, effective when large data sets naturally cluster around a central value.
- Probability equality across range:
- Equal across range: Uniform Distribution, where each outcome in a range is equally likely.
- Not equal across range: Poisson Distribution, suited for counting the occurrences of events over a fixed interval, where events happen with a known but uneven rate.
 Generated by github.com/unkokaeru/.
Generated by github.com/unkokaeru/.